
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a chemical produced by trophoblast (placental) tissue, which is present in early embryos and eventually becomes part of the placenta. hCG has many roles in pregnancy including – stimulating the ovaries to produce progesterone, triggers the body to create more estrogen, helps to thicken the lining of the uterus and tells your body to stop menstruating It also plays a role in boosting immunity to ensure the continuation of the pregnancy.
hCG is produced by the early cells of the placenta and due to its crucial role in supporting pregnancy, this hormone is commonly known as the “pregnancy hormone.”
A blood test used to evaluate hCG levels in early pregnancy is known as beta-hCG. It identifies the presence of an early pregnancy and, as the pregnancy continues, provides vital information about the pregnancy’s health.
Serial measurements of serum Beta Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG) in conjunction with Ultrasonography are used to identify or rule out an Ectopic Pregnancy (EP) in women who report with vaginal bleeding or abdominal discomfort in the first trimester. Rising levels of bhCG tell us about the health of the pregnancy. Significant increase in hCG may point to multiple pregnancies or even the presence of a pregnancy disease called Gestational Trophoblastic disease.
An initial value of 100 units is suggestive of implantation. Also, an hCG level of less than 5 mIU/mL is regarded as negative for pregnancy, whereas anything greater than 20 mIU/mL can suggest a positive result.
hCG levels after IVF embryo transfer
What is a normal hCG level after IVF?
Typically, a pregnancy test will come out negative if the hCG level is less than 5 mIU/ml. A positive pregnancy test will result from hCG levels greater than 20 mIU/ml.
Doubling of hCG levels every 48 hours and an increase in B hCG levels by 60% every fourth day are indicative of a healthy pregnancy.
By and large, the values of B hCG follow a pattern and individual variations exist. However, some variations are bound to be there.
What is hCG level in the first two weeks?
The greater the percentage of rise in hCG obtained two days after the initial beta, the greater the likelihood of success. Refer to the chart given below-
The first beta-hCG is usually done 14 days after ovulation or 14 days after embryo transfer. The levels are repeated every fourth day until the levels reach 20000. When this happens, an ultrasound scan is performed, and beta-hCG testing is halted.
A vaginal ultrasound (also called ‘internal ultrasounds’ or ‘transvaginal ultrasounds’) is performed using a transducer (probe) put into your vagina. Vaginal ultrasounds are performed
a) To show the location and size of the fetus.
b) To detect the baby’s heartbeat very early on in pregnancy.
c) To indicate if you are pregnant with one baby or more (such as twins or triplets)
d) To detect an ectopic pregnancy (when a fertilized egg implants outside the womb, generally in one of the fallopian tubes)
e) Determine the cause of any bleeding and whether the bleeding is the result of a miscarriage.
Usually, the first B hCG is done 14 days after ovulation or 14 days [ost the embryo transfer. The levels are repeated every fourth day till the levels cross 20000. Once this occurs, then an ultrasound scan is carried out, and B hCG testing is stopped.
What should the hCG level be 12 and 14 days after the embryo transfer?
After embryo transfer, the cut-off value for predicting clinical pregnancies on day 12 is 86.8 IU/mL, with 65.1% sensitivity and 74.7% specificity. On day 14, hCG levels of more than 200 mIU/ml are more likely to have continuous pregnancies and hCG levels greater than 600 are more likely to have a multiple gestation pregnancy.
The first hCG test typically takes about 2 to get back the results, and the waiting period can be a difficult time. Here are some ways you can make the overall process
a) Don’t isolate yourself, spend time with your friends and loved ones.
b) Keep living your normal lifestyle and try to keep yourself busy.
c) Talk about emotions you are feeling and don’t bottle them up.
d) Don’t focus too much on trying to spot symptoms or changes in your body.
Two week wait after IVF
There is no particular diet that is recommended in the first 2 weeks. A well balanced diet with micronutrients is recommended. It may be wise not to have a spicy and oily diet in order to prevent stomach upset and acidity. There are chances of constipation in early pregnancy. Hence fibre and green leafy vegetables are recommended. Isapgol is helpful in cases of mild constipation.
The first 2 weeks are important as this is the time when the embryo undertones implantation and also there are changes in immunity.
Fact check: fresh embryo transfer hCG trigger shots are administered during the stimulation phase
The hormonal support is different in a hormone replacement cycle which only consists of using estrogen and progesterone. In a stimulated cycle where a fresh embryo transfer is planned, injectable hCG is given every fourth or fifth day.
Fresh Embryo Transfer
In a fresh embryo transfer cycle, the embryo is transplanted during the same stimulation and egg retrieval cycle. The embryo(s) generated in that cycle are not frozen, but the best embryo is chosen after 5 days of culture to the blastocyst stage and then transplanted.
In order to assist early pregnancy, hCG injections are administered to encourage the corpus luteum to produce Progesterone.
Frozen Embryo Transfer
hCG injections are not necessary since they stimulate the corpus luteum to generate progesterone. Because a corpus luteum does not develop during a hormone replacement cycle, extraneous progesterone is administered.
A beta-hCG test can be performed as early as 9 days after the transfer, although it is recommended that the test be performed 12 to 14 days following the embryo transfer.
Pregnancy testing after IVF usually involves the beta hCG test done 14 days after ovulation, IUI or Embryo transfer.
The test measures the levels of Human Chorionic Gonadotrophin and whether the secreted levels are in the expected range.
The beta-hCG (-hCG) test determines the level of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in the blood. Aside from this, the test may be performed to evaluate fertility treatments and when there are suspicions that anything is wrong with a pregnancy.
What are normal hCG levels?
The levels of hCG are influenced by several factors, such as whether the embryo transfer is fresh or frozen, whether it’s done on day 3 or day 5, the timing of the test, and other variables. Typically, a pregnancy test will come out negative if the hCG level is less than 5 mIU/ml. A positive pregnancy test will result from hCG levels greater than 20 mIU/ml.
The The absence of implantation produces a negative pregnancy test
The presence of implantation produces a positive bhCG test .
Read more: 6 Symptoms Of IUI Pregnancy
FAQs About hCG Levels After Embryo Transfer
What do high hCG levels mean?
What do low hCG levels mean?
Why is hCG increase rate measured?
Why is slow rising hCG monitored?
Does hCG level go down during the first trimester?
When does decline of hCG level indicate a miscarriage?
Can beta hCG levels predict singleton or twins?
What if beta hCG is not rising or doubling?
Is it true that girl embryos have higher beta hCG?
Is it true that beta hCG may not be reliable for women with ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS)?
What are normal hCG results throughout pregnancy?
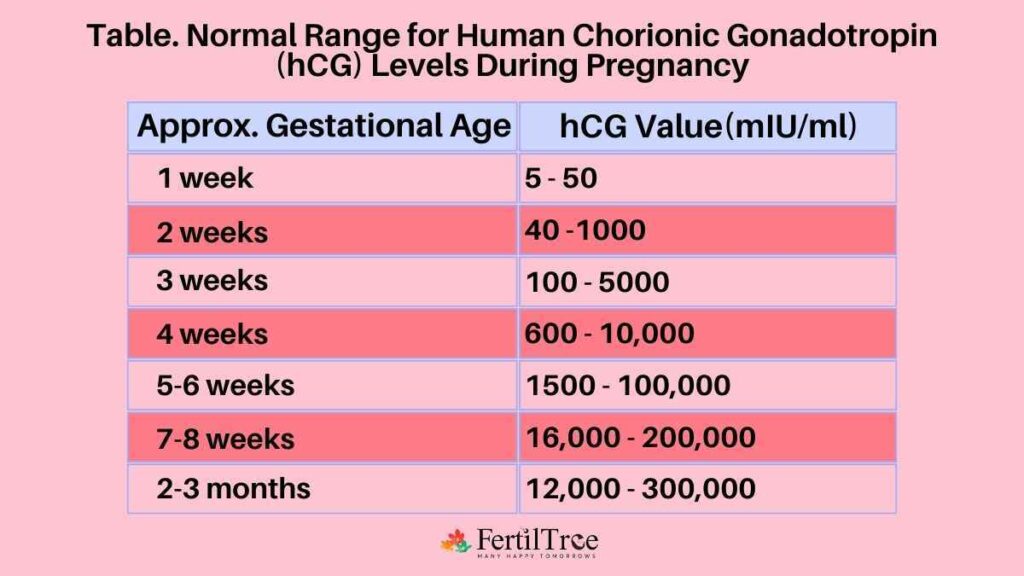
Normal Range for hCG Levels During Pregnancy Week by Week
Approximate Gestational Age – hCG Value (mIU/mL)
1 week – 5-50
2 week – 40-1000
3 week – 100-5000
4 week – 600-10,000
5-6 weeks – 1,500-1,00,000
7-8 weeks – 16,000-2,00,000
2-3 months – 12,000-3,00,000
SOURCE.
What if My hCG Levels Aren’t Over 100?
What should be the 2 weeks pregnant HCG levels?
Book A Consultation

