
Among the many procedures a woman goes through on her IVF journey, embryo transfer is one of the most crucial steps. This involves transferring embryos to a woman’s uterus and is the last step in the IVF process. Given this increasing trend in decking fertility in India, educating ourselves about assisted reproductive technology becomes increasingly necessary. With this in mind, and in hopes of making your IVF journey smoother, our blog for the day will focus on everything you need to know about embryo transfer.
What is embryo transfer?
An embryo transfer is a medical procedure wherein an embryo, is placed into the woman’s uterus. This is done with the intent that the embryo will get implanted in the uterine lining and lead to a pregnancy. It is the last part of an IVF process and at this part it is imperative that the embryo attach itself to the wall of the woman’s uterus.
To make sure that the placement is precise, your doctor will use an ultrasound scan. This painless procedure provides a clear image of the uterus, guiding the doctor in positioning a thin catheter that delivers the embryo. You might experience mild cramping during this process. The ultimate goal is creating an environment conducive to implantation and the joy of starting your own family.
Read more: Do’s and Don’ts after your Embryo Transfer
The Process Of Embryo Transfer
Embryo transfer, as mentioned earlier, is the final step in the IVF process. Here’s what you can expect during this process.
Your doctor will begin by inserting a speculum into your vagina so as to keep the vaginal walls open. Using ultrasound guidance for locating the position with precision, doctor will then insert a catheter through your cervix and into .the uterus. The embryo(s) are gently passed through this tube and into your uterus.
Typically, this procedure is pain-free and doesn’t require sedatives. However, you might feel some discomfort from the speculum or from having a full bladder, which is necessary for the ultrasound. The entire process doesn’t last long, and you can empty your bladder right after the procedure.
After the Embryo Transfer
You’ll need to schedule a follow-up appointment about two weeks later to check if the embryo has successfully implanted.
In the meantime, you might experience some cramping, bloating, and vaginal discharge after the procedure. These symptoms are normal and usually subside on their own.

When is IVF followed by Embryo Transfer needed
When natural fertilization is challenging or not possible, many couples turn to IVF and embryo transfer. Here are some reasons why you might need an embryo transfer:
- Ovulation Disorders: If you experience infrequent ovulation or if fewer eggs are available for successful fertilization.
- Damage to Fallopian Tubes: Your Fallopian tubes are the pathways for embryos to reach the uterus. If these tubes are damaged or scarred, fertilized eggs have a hard time reaching the womb safely.
- Endometriosis: In condition cells resembling those in the endometrial tissue grow outside the uterus, potentially affecting your reproductive function.
- Premature Ovarian Failure: If your ovaries fail prematurely, the release of eggs will be irregular.
- Uterine Fibroids: These benign tumors on the walls of your uterus can interfere with tge egg’s ability to implant, making pregnancy difficult.
- Genetic Disorders: Certain genetic disorders can prevent you from getting pregnant naturally.
- Impaired Sperm Production: Low sperm production, poor sperm movement, testicular damage, or semen abnormalities in your partner can also affect natural fertilization.
Types of Embryo Transfer
Embryos can be transferred in a fresh or a frozen cycle.
1. Fresh Embryo Transfer
This is the most straightforward approach. The fertilized eggs are cultured for 1 to 2 days, and the healthiest embryos are chosen for immediate transfer to your uterus.
2. Frozen Embryo Transfer (FET)
Currently, it is the most widely used method of embryo transfer where cryopreserved healthy embryos from a previous cycle can be used.. This offers flexibility and allows you to space out transfers or explore other options before transferring. Frozen embryos are thawed and transferred to your uterus during a carefully timed cycle.
3. Cleavage Stage Transfer (Day 3)
This method involves transferring embryos around day 3 of their development, following fertilization. Although this can be completed within a shorter time frame after egg retrieval Day 3 transfer is rarely used except in some circumstances.
4. Blastocyst Transfer (Day 5)
This particular technique allows the embryos to develop for 5 days, reaching a more advanced stage that closely resembles their natural state before implantation into the uterus. According to a study, Blastocyst Transfer is associated with increased pregnancy rates and lower miscarriage rates. Your doctor will guide you regarding the type of embryo transfer.
5. Single Embryo Transfer (SET or eSET)
In elective single embryo transfer (eSET), a single embryo is implanted in the uterus during IVF, even if more embryos are available. A study of 156 women found fresh single embryo transfers (41.3% live birth rate) had a significantly higher success rate than double transfers (32.6%) in subsequent frozen cycles.
6. Transfer of multiple embryos
This is when two or more embryos are implanted to the uterus during IVF. It can increase pregnancy chances but also significantly raises the risk of multiples (twins and higher order multiple pregnancies).
7. Assisted Hatching (AH)
Assisted Hatching (AH) is a technique where a tiny opening or thinning is created in the zona pellucida in a laboratory setting. This could be particularly helpful for women undergoing IVF at an advanced reproductive age. The idea is to potentially increase the chances of successful implantation by making it easier for the embryo to hatch.
Key Decisions Regarding Embryo Transfers
| Component | Impact on Treatment | Impact on Cost |
| 1 or Fewer Embryos (Fresh) | Frozen and fresh embryo transfers can both be suitable options. While fresh transfers may be quicker, frozen transfers might offer higher success rates and allow for more logistical planning, although they typically involve a one-month wait. | Fresh embryos are more often than not included in the basic price of embryo transfer. |
| 1 or 2 Embryos (Frozen) | Transferring one embryo is generally the preferred approach. This helps maintain overall success rates and minimizes risks for both the mother and the developing baby. However, transferring two embryos might be considered in specific circumstances. | Very little impact on overall cost. Clinics typically charge by number of transfers, not the number of embryos transferred. |
| Medications | Medications are generally recommended to optimize embryo transfer success. However, natural cycles without medication can be an option if the woman naturally develops a good uterine lining. Immune modifying medications might be considered for those with a history of recurrent implantation failures or miscarriages. | Medication may add to the cost of treatment..the cost would be less if using a natural cycle, |
| Genetic Testing Before Transfer | Could aid in reducing the chances of miscarriage, genetic disorders,and implantation failure. | Can increase cost. |
When Does Embryo Transfer Occur?
The timing of the transfer of your embryos can vary during IVF.. Every cycle is unique, influenced by various factors closely monitored by your doctor.
Fresh vs. Frozen Transfer Timing:
- Fresh Transfer: This cycle starts with stimulation medication, typically on days 3 or 5 of your menstrual cycle (if applicable). The transfer date depends on when your eggs are retrieved and the embryo’s development stage. Monitoring with ultrasounds and blood tests might adjust the retrieval date or require additional stimulation days. Most transfers happen at the blastocyst stage (5 days after retrieval). However, embryo development can vary, and transfers on day 7 after retrieval are rarely carried out.
- Frozen Transfer (FET): FET cycles are customized based on your individual response to medications and uterine lining development. The timing of progesterone introduction is important and the transfer date hinges on when progesterone starts:
- Cleavage stage embryos: Transferred 4 days after progesterone begins.
- Blastocyst embryos: Transferred 6 days after progesterone begins.
What You Can Do Before Embryo Transfer To Improve Chances Of Success
There are quite a few steps you can take before an embryo transfer to enhance the likelihood of a successful outcome. Here are key steps you can take 30-90 days beforehand. Do bear in mind that this timeframe is crucial as eggs enter their final development phase roughly 90 days prior to ovulation, thus influencing embryo quality.
Diet & Supplementation
- Diet: Consider a diet low in fugues as these cause inflammation throughout your body, including the reproductive system.
- Supplements: Explore fertility supplements like CoQ10/ubiquinol, inositol, and Vitamin D. These can be beneficial for both you and your partner. Several companies offer comprehensive fertility supplement packages, simplifying the process.
Prescription Medications
If you have a history of failed implantation, certain medications can improve transfer outcomes. These include: Intralipids, low-dose aspirin, human growth hormone antibiotics,Prednisolone, hCG, IVIG, Filgrastim, Viagra, Antihistamine and, Metformin. Do discuss these options with your doctor to determine if they are right for you.
Surgical and Mefical Treatment
- Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: PRP uses concentrated platelets from your blood to enhance healing and tissue growth. It can be used to support egg development and improve endometrial thickness and receptivity.
- Endometrial Scratching: This minimally invasive procedure involves “scratching” the uterine lining, which can trigger the release of chemicals that promote healing and potentially improve lining development in subsequent cycles.
- Intra-uterine hCG: Adding a small amount of hCG to the uterus before transfer is believed to increase implantation rates. Your doctor can advise if this is right for you.
- Endometrial Receptivity Analysis (ERA): This test helps determine your ideal window of implantation to optimize transfer timing and prevent implantation failure.
- Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy: These are minimally invasive procedures that can diagnose and correct conditions like endometriosis, fibroids, abnormal growths, and adhesions that might be impacting fertility.
Holistic Therapies
Acupuncture: Research suggests that acupuncture might modestly improve clinical pregnancy rates in some women undergoing IVF, particularly those with a history of failed cycles after multiple treatments.
Yoga: Practicing yoga has been instrumental in improving blood flow to reproductive organs, lessening stress, and balancing your immune system.
Note: Before trying any of the tips shared above, it is advised that you consult your doctor first.
What To Expect During Embryo Transfer
Here’s a rundown of what to expect before and during your embryo transfer:
Before the Transfer:
- The transfer will occur in the sterile Ooeration Theatre room at the clinic with your doctor, nurse and embryologist present.
- While anesthesia isn’t typical, medication to ease you mentally and relax your uterus might be offered.
- Take the prescribed medications as instructed. Some doctors advise not using vaginal suppositories the morning of the transfer unless otherwise advised.
- Your doctor and embryologist will double-check your identity and embryo details for accuracy.
During the Transfer:
- The embryologist will carefully place the embryo into the transfer catheter.
- A speculum will be used to visualize and clean your cervix.
- Using ultrasound guidance, the catheter carrying the embryo will be inserted through your cervix and into your uterus.
- Once positioned, the embryo will be gently deposited in your uterus.
- Similar to a pap smear, you might feel some minor discomfort during speculum insertion or catheter placement, but it shouldn’t be painful.
What To Do After Embryo Transfer to Increase Chances of Success
While every clinic might have slightly different instructions, here’s a general guide on what to expect after an embryo transfer:
Relax and Take Care of Yourself:
- You can go home and relax.
- While bed rest was once recommended, it is no longer considered necessary. You can return to your normal routine but avoid strenuous exercise and heavy lifting.
- Get a good night’s sleep and focus on de-stressing yourself eith activities that you enjoy.
- Maintain a positive outlook ehike waiting for your pregnancy test.
- Try not to obsess over do’s and don’ts, focus on your well-being.
Maintain Healthy Habits:
- Continue taking all medications prescribed by the concerned doctor.
- Eat a healthy die.
- Stay active, but avoid strenuous exercise.
Listen to Your Body:
- Avoid sexual intercourse for now a short period while awaiting the pregnancy results.
- Steer clear of extreme temperatures like hot baths, saunas, or heating pads, as they can raise your body temperature.
Success Rates Of Embryo Transfers
The success rate of embryo transfer depends on a number of factors, including patient age and the cause of infertility.
According to the 2020 National ART Summary by CDC, the percentage of embryo transfer cycles that resulted in live birth delivery of one or more live infants generally decreased as the age of the woman increased. This is because the likelihood of a fertilized egg implanting is related to the woman’s age. On the other hand, embryo transfer cycles using donor eggs resulted in a higher percentage of live births across all ages (range: 37.6% to 48.5%) because egg donors are usually in their 20s or early 30s and have higher fertility rates.
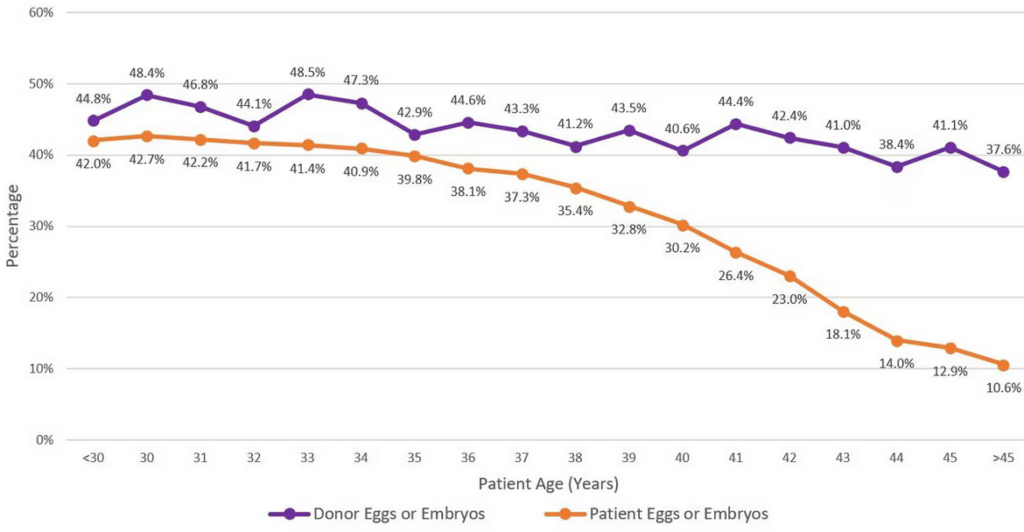
Image Source: www.cdc.gov
In another study, the ongoing pregnancy rate was higher in the frozen embryo group (52%) compared to the fresh embryo group (45.3%). This suggests that freezing embryos before transfer may improve the chances of a successful pregnancy by keeping the lining in phase.
Benefits And Risks Of Embryo Transfers
Choosing between fresh and frozen embryo transfers involves weighing various factors. Both methods offer advantages and disadvantages. It’s important to note that while cramping and vaginal bleeding are common after embryo transfer, severe side effects like uterine perforation or infection are extremely rare. Choosing a reputable fertility clinic with a good safety record is an absolute must.
In this section, let’s take a look at both Fresh Embryo Transfers and Frozen Embryo Transfers (FET) so that you will have all the necessary information required.
Fresh Embryo Transfers
Pros:
- Faster path to pregnancy: Fresh transfers involve minimal waiting time (around 5 days) between egg retrieval and embryo implantation.
- Cost: Insurance may not cover embryo cryopreservation (freezing), making fresh transfers financially attractive for some patients.
Cons:
- Hormonal impact: Fresh transfers require ovarian stimulation medication during IVF, which can lead to high estrogen levels. This may dysregulste the endometrium.
- Unsuitable for certain conditions: Fresh transfers may not be ideal for women who have elevated progesterone levels or those at risk of Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS) due to the additional medications involved.
Frozen Embryo Transfers (FET)
Pros:
- Improved success rates: Frozen transfers allow for preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) of embryos before implantation. This can increase pregnancy success rates and reduce the risk of chromosomal abnormalities in the baby.
- Flexibility and convenience:
- Rest and recovery: You can choose FET to give your body time to recover after egg retrieval.
- Future family planning: Leftover embryos from a previous cycle can be used for FET, avoiding additional egg retrieval procedures. Frozen embryos can remain viable for over a decade, allowing you to choose a FET cycle at a later date, even after an unsuccessful fresh cycle.
- Hormonal balance: FET allows time for your hormones to regulate after the initial fertility medications used for egg retrieval.
- Addressing medical concerns: FET is a good option if you have OHSS or elevated progesterone levels during ovarian stimulation, as it avoids further hormonal stimulation.
Cons:
- Cost: Cryopreservation (freezing) of embryos may come with additional costs.
- Waiting time: FET involves a longer wait compared to fresh transfers, as the embryo is frozen.
How Much Does an Embryo Transfer Cost?
The cost of IVF in India varies depending on factors like location, clinic, and chosen procedures. We’ll explore these factors in detail later. At FertilTree, Frozen Embryo Transfer costs range from Rs 85.000 to Rs. 1,50,000
Empowering Yourself Through Knowledge
Embryo transfer, the final step in IVF, offers a worthwhile path to family building. Understanding the different embryo transfer types (fresh, frozen, etc.) and their pros and cons empowers you to make an informed decision.
Related Articles:
- How Does Clomid Work Treating Infertility Patients?
- hCG Levels After IVF Embryo Transfer
- Do’s and Don’ts after your Embryo Transfer
- What is embryo grading? Day 3, Day 5, Success Rates
References:
“Embryo Transfer | Emory School of Medicine.” Med.emory.edu, med.emory.edu/departments/gynecology-obstetrics/patient-care/patient-education/embryo-transfer/index.html.
“Secondary Infertility: Causes, Statistics, Treatment Options, and More.” Www.medicalnewstoday.com, 30 June 2022, www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/secondary-infertility.
Wang, Ange, et al. “Freeze-Only versus Fresh Embryo Transfer in a Multicenter Matched Cohort Study: Contribution of Progesterone and Maternal Age to Success Rates.” Fertility and Sterility, vol. 108, no. 2, 1 Aug. 2017, pp. 254-261.e4, www.fertstert.org/article/S0015-0282(17)30363-1/fulltext, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2017.05.007.
Westergaard, Lars G., et al. “Acupuncture on the Day of Embryo Transfer Significantly Improves the Reproductive Outcome in Infertile Women: A Prospective, Randomized Trial.” Fertility and Sterility, vol. 85, no. 5, May 2006, pp. 1341–1346, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2005.08.070. Accessed 19 Mar. 2023.
Xie, Zheng-yun, et al. “The Effects of Acupuncture on Pregnancy Outcomes of in Vitro Fertilization: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.” BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine, vol. 19, no. 1, 14 June 2019, https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-019-2523-7. Accessed 11 Mar. 2021.
“2020 National ART Summary | CDC.” Www.cdc.gov, 21 Feb. 2023, www.cdc.gov/art/reports/2020/summary.html.

