Teratozoospermia (also called Teratospermia) is the production of morphologically abnormal sperm, which are often functionally deficient. According to WHO 2010, criteria when more than 96% of the sperms produced have morphological defects of the head, midpiece, or tail, then it is considered a case of teratozoospermia. If at least 4% of the sperm are morphologically normal, then the male is fertile. Teratospermia reflects a defect in sperm maturation in the testis.
Teratozoospermia may be associated with male infertility. It is a difficult task to pinpoint a reason for this condition—factors like Genetics, Diabetes, Smoking, Varicocele, and Age impact sperm morphology. Radiation and chemotherapy have an impact on spermatogenesis and lead to teratozoospermia.
Teratozoospermia Types, Symptoms & Treatment
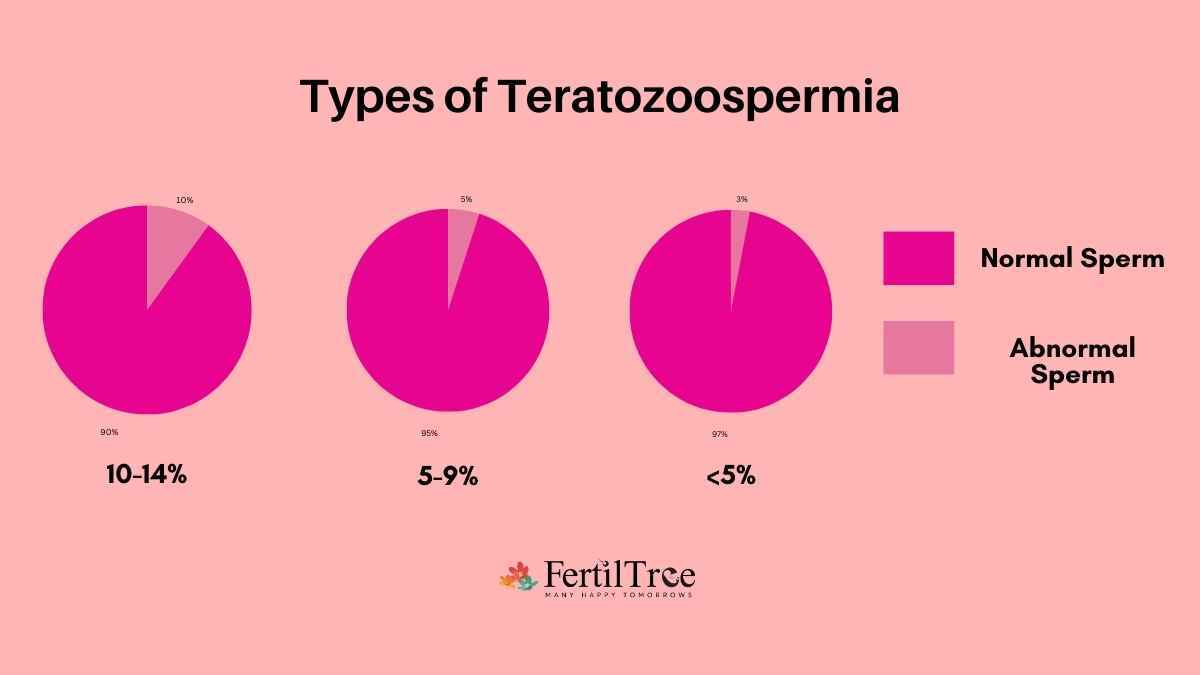
What are the Types of Teratozoospermia
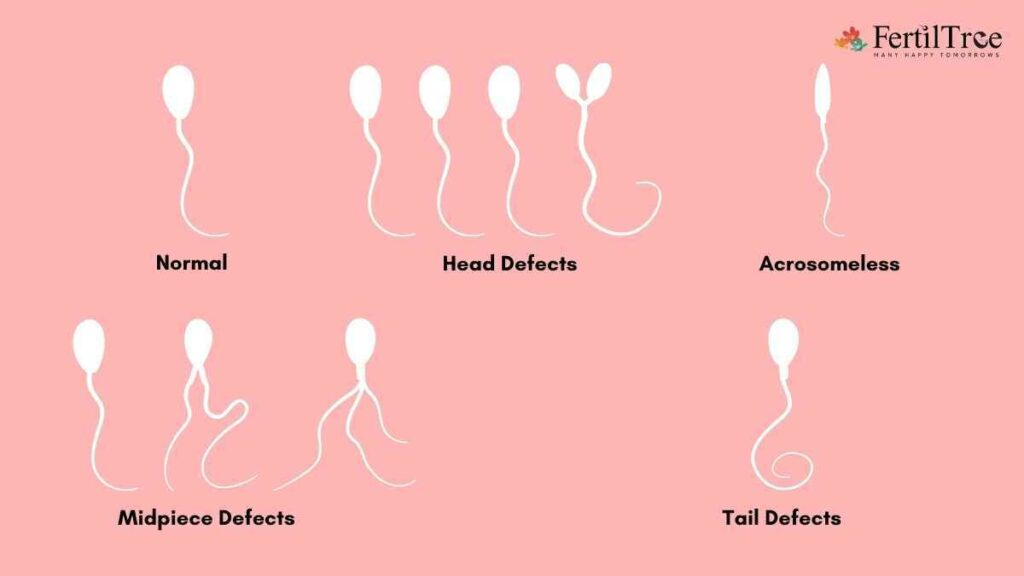
Teratozoospermia is classified into different types depending on the particular abnormalities found in sperm morphology. Some common abnormalities are-
- Head Defects – The form or structure of the sperm head is abnormal in this kind of teratozoospermia. Large or tiny heads, tapering heads, multiple heads, or pyriform (pear-shaped) heads are examples of head deformities.
- Tail Defects – Tail defects are abnormalities in the structure or function of the sperm tail. Coiled or curled tails, extremely long or short tails, double tails, or nonexistent tails (acephalic sperm) are all examples of tail abnormalities.
- Neck or midpiece defects – Neck defects in teratozoospermia include excessively long or short necks, thicker necks, or the presence of vacuoles (small fluid-filled cavities) in the neck region.
- Midpiece Defects – The midpiece of the sperm is in charge of producing the energy needed for movement. Teratozoospermia can arise when the midpiece is abnormally shaped, such as when it is enlarged or when vacuoles are present in the midpiece area.
- Multiple defects: In this type of teratozoospermia, the sperm has multiple defects, perhaps all of the above mentioned, and this leads to a severe case of teratozoospermia.
An andrology technician or embryologist can identify the type of teratospermia.
What are the signs of Teratozoospermia? How is it diagnosed?
Teratozoospermia is the most common cause of male infertility; generally, abnormal sperm have difficulty fertilizing an oocyte. Typically, it is diagnosed through a semen analysis, which will evaluate the number, shape, and motility of the sperm cells. A diagnosis of teratozoospermia can be made if more than 96% of the sperm cells are abnormally shaped.
Teratozoospermia Treatment options
Teratospermia, due to controllable factors such as inflammation, infection, diabetes, or unhealthy habits, has a very high chance of being treatable. Teratozoospermia that is genetic or a result of irreversible injury, surgery, or condition, the chances of possible treatment become very low. Certain supplements supporting male fertility, such as omega-3 fatty acids, L-carnitine, antioxidants, Zinc, and vitamin E, can aid in correcting this condition.
Teratozoospermia and pregnancy rates, how are they related?
Pregnancy rates with teratozoospermia differ depending on the severity of the condition, other parameters such as sperm count and motility, and the presence of other fertility issues of the male or female partner.
Is it possible to get pregnant with Teratozoospermia?
Yes, it is possible if the other sperm parameters are normal.
Can IVF be successfully done with teratozoospermia?
In patients with mild teratospermia, with a normal sperm count and sperm motility, Intrauterine Insemination (IUI) may be considered as a fertility treatment. In the case of moderate to severe teratospermia, IVF is the best treatment option. IMSI (Intracytoplasmic Morphologically Selected Sperm Injection) uses a high magnification imaging method to see sperm shape in detail; it can enhance the possibility of further success.
Is it possible to treat teratozoospermia naturally?
Adopting a healthy lifestyle would be the first step in curing teratozoospermia. Factors that influence testosterone levels have the most significant impact on sperm number and quality.
Medical conditions that adversely impact include inherited genetic disorders, infections, and tumors. Lifestyle factors like smoking, excessive alcohol, and electromagnetic radiation from the use of laptops, mobile phones, and drugs have adverse effects. Correcting the lifestyle factors has a major impact on improving sperm production.
Adopting a healthy diet and exercise regime, preventing or limiting exposure to plasticizers, and intake of antioxidant supplements helps in achieving a healthy sperm count.
Can teratozoospermia resolve on its own?
If the causative reason is physical stress, injury to testicles, smoking, or alcohol, then it could be resolved with lifestyle changes and medication.
When is a man’s sperm considered healthy?
When the sperm has the following features
Smooth-rimmed, oval-shaped head between 2.5 to 3.5 μm wide and 5 to 6 μm long and free of large vacuoles. Acrosome tip that covers between 40 and 70 per cent of the sperm head
Midpiece should be about the same length as the head but much slimmer
Tail uncoiled, 45 μm-long, should be thinner than the sperm head and the midpiece.
Read more: How to make sperm stronger for pregnancy?
What is 0 morphology?
Not all of an individual’s sperm look exactly alike. Abnormalities in sperm size and shape can occur in the head, midpiece, or tail. Having a large number of abnormally formed sperm in a sample and a low number of normal forms are signs of teratozoospermia. The range can vary, but typically a normal sperm morphology ranges between 4 and 14 percent normal forms. A score below 4 per cent may mean it takes longer than normal to achieve pregnancy.
A result of 0 percent normal forms usually means Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) may be necessary for conception.
Read more:
Book A Consultation

