
Failed implantation of a fertilized egg is a significant concern for those undergoing fertility treatments. This process is one extremely important step for a successful pregnancy, and when it doesn’t occur, it can be a source of distress. In our blog for the day, we will explore the reasons behind the necessity of fertilized egg implantation, the process itself, the prevalence of implantation failure, and the symptoms and factors contributing to it. We will also discuss risk factors, preventative measures, and when to seek medical advice.
Unsuccessful Implantation of a Fertilized Egg Meaning
Unsuccessful implantation of a fertilized egg, often called failed implantation, occurs when the fertilized egg cannot attach to the lining of the uterus during the early stages of pregnancy. This attachment is imperative as it allows the developing embryo to receive essential nutrients and oxygen from the mother. Without this connection, the pregnancy cannot progress.
Read more: Do’s and Don’ts after your Embryo Transfer
How Common is Implantation Failure?
As per an article published on Apricity’s website, approximately 5% of people undergoing IVF face implantation failure during at least two consecutive attempts.
A significant portion of these cases—about 75%—are attributed to issues with implantation. When this occurs three or more times, it is classified as “repeated implantation failure,” indicating persistent underlying challenges that must be addressed.
Another article suggests that a significant portion of fertilized eggs, ranging from 30 to 50 percent, fail to implant in the uterine lining.
According to another study, 10% of couples undergoing in vitro fertilization (IVF) and embryo transfer experience recurrent implantation failure (RIF).
As you can decipher from these findings, unsuccessful implantation is common in IVF.

Why Do Fertilized Eggs Need to be Implanted?
Implanting a fertilized egg into the uterine lining is a critical step in the pregnancy. This process allows the embryo to receive the nutrients and support it needs to grow and develop.
The Importance of the Uterine Lining
The uterine lining, or endometrium, must be thick and receptive to successful implantation. This lining changes the menstrual cycle, preparing to support a pregnancy or shed during menstruation.
Also Read: How to Improve Uterine Lining For IVF
How are Fertilized Eggs Implanted?
The Journey to the Uterus
After fertilization, the egg goes down the fallopian tube towards the uterus. This journey typically takes about five days, during which the fertilized egg, now called a blastocyst, begins to divide and grow.
Implantation: A Crucial Connection
Implantation happens as soon as the blastocyst attaches itself to the uterine lining. This connection is vital as it enables the embryo to access the mother’s blood supply for nutrients and oxygen, essential for continued development.
Symptoms of Failed Implantation
Identifying failed implantation can be challenging, as the early signs may be subtle and often resemble those of a normal menstrual cycle. Here are some potential indicators of unsuccessful implantation:
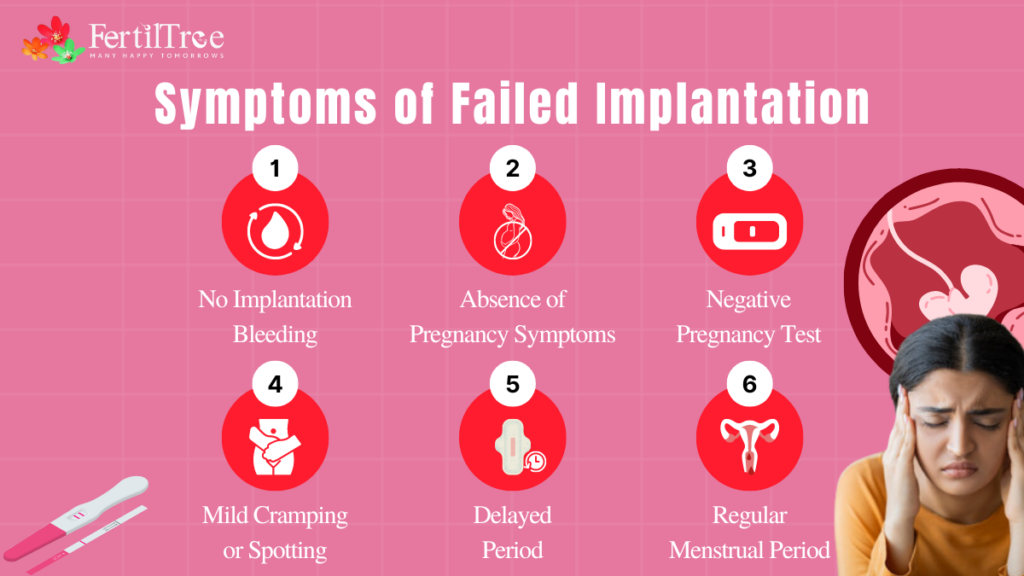
- No Implantation Bleeding: Some women experience light spotting or bleeding when the fertilized egg attaches to the uterine lining. If this doesn’t happen, it could suggest a failed implantation, although not all women experience implantation bleeding.
- Absence of Pregnancy Symptoms: If you do not notice early pregnancy symptoms such as breast tenderness, fatigue, or increased sensitivity to smells, it might indicate that implantation has not occurred.
- Negative Pregnancy Test: A negative pregnancy result on a home pregnancy test taken after a missed period often means that implantation was not successful. But, false negatives could also happen if the test is taken too early or is not performed correctly.
- Mild Cramping or Spotting: Some women may experience mild cramping or spotting, which could indicate unsuccessful implantation.
- Delayed Period: A delayed period without other signs of pregnancy might indicate failed implantation.
- Regular Menstrual Period: Getting your regular menstrual period indicates that implantation did not occur.
Factors Affecting Implantation
Several factors can contribute to implantation failure, including:
- Embryo Quality: Poor embryo quality can hinder successful implantation.
- Uterine Problems: Issues such as fibroids, polyps, or a thin endometrial lining can prevent the embryo from attaching.
- Chromosomal or Genetic Abnormalities: Abnormalities in the embryo’s chromosomes or genes can lead to failed implantation.
- Lifestyle Factors: Factors such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and high-stress levels can negatively impact implantation.
Also Read: Foods To Increase Sperm Count and Motility
Additional Symptoms and Indicators
Vaginal Bleeding and Stomach Pain: Unexpected vaginal bleeding and stomach pain can be signs of failed implantation or other reproductive issues.
Note: It’s important to remember that these signs are not definitive proof of failed implantation. If you have concerns about your pregnancy, consulting with a fertility specialist is always the best course of action.
Factor Of Implantation Failure
Implantation failure can stem from issues in the mother, the embryo, or both:
- Maternal Factors:
- Uterine Abnormalities: Physical problems in the uterus, like polyps or fibroids, can hinder implantation.
- Immune System: An unbalanced immune response might reject the embryo.
- Endometrium: A thin or unresponsive uterine lining can prevent proper implantation.
- Embryonic Factors:
- Genetics: Chromosomal abnormalities in the embryo can lead to implantation failure.
- Development: Problems with embryo development, like abnormal cell division, can prevent implantation.
- Male Contribution: Poor sperm quality, such as DNA fragmentation, can affect embryo health.
Risk Factors for Failed Implantation
Several factors can increase the chances of implantation failure. Here’s a breakdown of some of the common ones:
Age: Advanced maternal age is one of the most significant risk factors for failed implantation. As females age, the quality as well as the quantity of their eggs decline, which can lead to difficulties in achieving and maintaining a pregnancy. Women over the age of 35 may face higher risks of implantation failure due to decreased egg quality and potential uterine changes.
Existing Health Conditions: Certain health conditions can negatively impact implantation. Conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), endometriosis, thyroid disorders, and diabetes can interfere with the hormonal balance and uterine environment necessary for successful implantation. Proper management of these conditions is crucial to improve the chances of a successful pregnancy.
Previous Pregnancy Complications: A history of pregnancy complications, such as miscarriages, ectopic pregnancies, or preterm births, can indicate underlying issues that might affect implantation. These complications could be due to structural abnormalities of the uterus, hormonal imbalances, or other medical conditions that need to be addressed to improve the chances of successful implantation.
History of Implantation Failure: Repeated implantation failures can indicate persistent underlying problems that must be identified and managed. Factors such as poor embryo quality, uterine abnormalities, or immunological issues could contribute to repeated failures. Identifying and addressing these factors through comprehensive testing and tailored treatments can increase the likelihood of successful implantation in future attempts.
What Can You Do to Prevent Failed Implantation?
There are quite a few factors that can cause infertility, as well as failed implantation after IVF, which are beyond your control. However, you should not feel hopeless if you’ve had difficulties conceiving. Optimizing your body’s health can improve the chances of IVF success. Here are some steps you can take:
Change Your Lifestyle Behaviors: Smoking and frequent alcohol consumption negatively affect your health and your body’s ability to sustain a viable pregnancy. Even if you do not smoke or drink regularly, your partner’s habits can contribute to male infertility. Smoking and excessive alcohol use can damage healthy sperm, reducing the likelihood of producing a viable embryo through IVF.
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Weight plays a huge role in one’s ability to achieve pregnancy during the IVF procedure. Both being overweight and underweight can cause issues with implantation. Maintaining a healthy weight by leaning towards a balanced diet while also exercising regularly can significantly boost your body’s readiness for a healthy pregnancy.
Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT): Preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) can help to identify potential genetic abnormalities that might lead to failed implantation before embryo transfer. This testing helps select embryos with the best chance of successful implantation and development.
Screen for Underlying Health Conditions: Underlying health conditions can hinder embryo implantation. These may include uterine abnormalities, hormonal imbalances, thyroid disorders, diabetes, and previous infections. A comprehensive health screening before attempting IVF can enable your doctor to recommend interventions to increase the procedure’s success rate.
When other fertility treatment options have been exhausted, your doctor may suggest surgical, immunomodulatory, or hormonal treatments to improve the likelihood of implantation. The success rates of these treatments vary, and the associated costs can be significant.
When to See a Doctor
Early consultation with a fertility specialist is an absolute must if you have concerns about implantation or your pregnancy journey. Here are some key situations to consider:
- Recurrent Pregnancy Loss: Experiencing two or more consecutive miscarriages raises a red flag. Consulting a leading fertility specialist in Mumbai can help identify the root cause and explore potential treatments like those offered at some of the best IVF clinics in Mumbai.
- Irregular Menstrual Cycles: Consistently irregular periods might indicate hormonal imbalances or other conditions impacting fertility and implantation. A fertility specialist in Mumbai can evaluate your situation and recommend appropriate solutions.
- Severe or Unusual Symptoms: Severe pain, heavy bleeding, or other concerning symptoms during the potential implantation window warrant immediate medical attention. A fertility specialist in Mumbai can rule out any complications or health concerns.
- Difficulty Conceiving: If you’ve been trying to conceive for over one year (or six months if you’re over 35) without success, seeking professional help is advisable. Dr. Firuza Parikh is a well known fertility specialist at Jaslok Hospital in Mumbai can assess potential fertility issues and guide you towards suitable options, including advanced treatments offered at some of the best IVF clinics in India.
How Can FertilTree Help You
We, at FertilTree, know what a rollercoaster ride it can be when undergoing an IVF treatment. At our state-of-the-art clinic, we aim to create a positive and supportive experience for all our patients. With some of the best fertility doctors and our team of helpful hands, we treat each patient based on their unique needs and provide specialized treatment options for them accordingly.
If you have experienced one or more implantation failures, we are here to help. All you have to do is call +91 9920842070 to make an appointment.
Found this post informative? Read more insightful Blogs at FertilTree. For expert guidance on fertility treatments, visit Dr. Firuza Parikh’s profile and explore the wealth of resources available on FertilTree.
For further inquiries, you can reach out to us at [email protected].
FAQs on Symptoms of Failed Implantation of Fertilized Egg
My first cycle of IVF failed. What should I do next?
What are the most stressful stages of IVF?
How long is the process of IVF?
Sources:
Simon, Alex, and Neri Laufer. “Assessment and Treatment of Repeated Implantation Failure (RIF).” Journal of Assisted Reproduction and Genetics, vol. 29, no. 11, 1 Nov. 2012, pp. 1227–1239, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3510376/, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-012-9861-4.
Ma, Junying, et al. “Recurrent Implantation Failure: A Comprehensive Summary from Etiology to Treatment.” Frontiers in Endocrinology, vol. 13, 5 Jan. 2023, p. 1061766, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9849692/, https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2022.1061766.
Book A Consultation

