
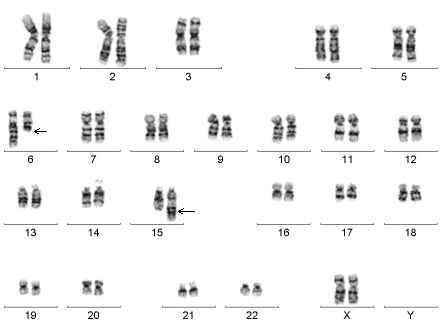
Infertility Management
Indications for Cytogenetic Analysis:
- Couples with repeated spontaneous miscarriages
- Couples with primary infertility
- Males with oligozoospermia and azoospermia
- Males with hypogonadism, breast development and lack of facial hair
- Women with primary amenorrhoea, short stature, and streak gonads.
Sample: 2 ml Blood in sodium heparin vaccutainer (Green top tube), transported at room temperature. No fasting is required.

Routine analysis of sperm chromosomes is not feasible in clinical practice. However, interphase FISH on spermatozoa offers an accurate and reliable method of analysis even in the presence of a low sperm count.
The percentage of sperm with hypo/hyperhaploidy (less chromosomes / more chromosomes) is calculated to counsel the couple.
Sample : Fresh / Frozen-thawed semen sample.
Outstation samples are also accepted.
Note: All samples should be accompanied with a copy of the semen analysis report at the time of sample collection which should include the name of the patient, age, count, motility and morphology of the sperm.
Y chromosome micro-deletions like DAZ (deletion in azoospermia) and RBM (RNA binding motif gene) cause spermatogenic defects. In the Yq arm (long arm of the Y chromosome), intervals V and VI comprise an Azoospermia Factor (AZF) which contains the DAZ and RBM genes. Several genes have been identified within this region and have been proposed candidates for infertility. We can check for 29 different micro-deletions including 5 partial deletions in the AZF region by multiplex PCR.
If Y chromosome microdeletions are seen only in the AZFc region, there is a good chance that TESA will be successful. However, if microdeletions are seen in the AZFa and AZFb regions, the chances of success after TESA are extremely low.
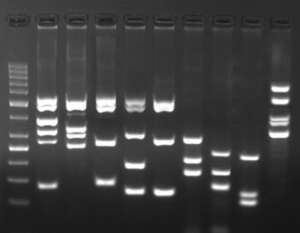
Multiplex PCR for Y microdeletion detection
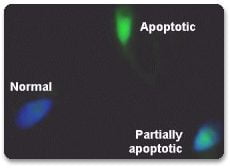
The Sperm DNA Fragmentation Index (DFI) test is used to determine whether the male partner of an infertile couple has a high, fair, or poor fertility potential by studying fragmentation of his Sperm DNA.
Apoptosis is a mode of programmed cell death based on a genetic mechanism that induces a series of cellular, morphological and biochemical alterations, resulting in fragmentation of the genomic DNA. The sensitive TUNEL method is based on the detection of single and double stranded DNA breaks occurring at early stages in apoptosis.
After an enzymatic reaction, the fluorescein label incorporated at the damaged sites of DNA is visualized by fluorescence microscopy. The apoptotic sperm appear greener, while the normal non-apoptotic sperm take up more of the DAPI stain and appear blue. Partially apoptotic sperm will appear partially blue and green. This test allows the detection of apoptosis at the single cell level and may serve as an indicator for use of antioxidants prior to IVF.
The DFI is a ratio expressed as a percentage of sperm which has fragmented DNA due to apoptosis divided by the total number of sperm analyzed.
The sperm apoptosis test provides a reliable analysis of sperm DNA integrity that may help to identify men who are at a risk of failing to initiate a healthy ongoing pregnancy. It may help in the clinical diagnosis, management and treatment of male infertility and could be of prognostic value in assessing the outcome of various methods of Assisted Conception.
Apoptosis may not completely eliminate the cell’s competence for fertilization. Hence, an apoptotic spermatozoon, possessing high levels of DNA fragmentation, can fertilize the oocyte using ICSI. Such a pregnancy with DNA damage in the sperm may lead to miscarriage.
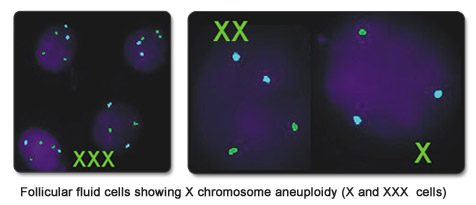
Follicular fluid is a novel source of gonadal cells for detection of low-grade mosaicism in the ovaries. Study of gonadal cells present in the follicular fluid of women undergoing IVF can determine the chances of a successful pregnancy. If there is evidence of gonadal mosaicism, the chances of a live birth could be low. Mosaicism for the X chromosome can be detected rapidly by FISH on follicular fluid cells and can be one more indication for Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT) in the same and subsequent cycles.
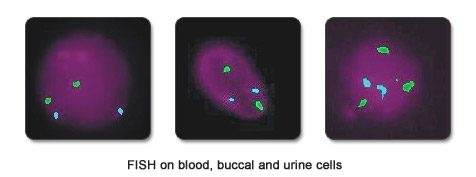
Mosaicism is the presence of chromosomally normal and abnormal cells in the same individual. The percentage of mosaicism is known to vary in different tissues. We can easily study buccal, urine and blood cells by FISH. When more than 5% aneuploidy for the X chromosome is detected in the follicular fluid cells derived from the ovary, we check for aneuploidy in these other tissues as well.
MTHFR Mutation testing:
Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase (MTHFR) Deficiency is the most common genetic cause of elevated levels of homocysteine in plasma (Hyperhomocysteinemia).
Clinical Significance and Utility:
Hyperhomocysteinemia is a risk factor for arterial disease and venous thrombosis. Homocysteine levels are affected by nutritional and genetic factors.
- Two mutations (C677T and A1298C) in the MTHFR gene have been associated with increased levels of circulating homocysteine. Homozygosity for the C677T mutation or compound heterozygosity for C677T and A1298C is associated with reduced MTHFR activity. Decreased MTHFR activity leads to hyperhomocysteinemia and lowers plasma folate levels. Homozygosity for 677C>T may increase risk for venous thrombosis and pregnancy complications (pre-eclampsia, placental abruption, intrauterine growth restriction).
- In case of homozygosity for the C677T mutation or compound heterozygosity for C677T and A1298C mutations and homocysteine results, physicians can develop dietary and medical recommendations – increased intake of methylfolate alone or in combination with vitamins B6 and B12 are recommended.
Prothrombin Mutation testing:
Prothrombin or Factor II is a protein in the blood that is required for the formation of fibrin in blood clotting process.
Clinical significance and utility:
- Low levels of prothrombin causes frequent bleeding whereas high levels cause unwanted blood clots.
- A history of recurrent pregnancy loss or stillbirth, may be indicative of an underlying thrombophilia (the blood has an increased tendency to clot).
- Mutation G20210A in the prothrombin gene leads to increased levels of prothrombin which ultimately leads to increased risk of blood clotting. Individual with this mutation have an increased risk of developing Deep Vein thrombosis (DVT).
Indications for Testing:
Indications for testing as part of the screening for thrombophilia include: venous thromboembolism (especially if in an unusual site), deep vein thrombosis during pregnancy, venous thromboembolism while on oral contraceptives, fetal death after 10 weeks gestation, fetal growth restriction and/or preclampsia, and/or family history of stroke, pulmonary embolus, deep vein thrombosis in first degree relatives under the age 50.

