Hematological and Other Malignancies
Several specific rearrangements occur in the chromosomes in different types of leukemias like CML, CLL, AML, ALL, MPD and MDS. The treatment varies in certain abnormalities. Hence karyotyping is essential to find out the type of abnormality present in individual cases. A bone marrow sample (which has actively dividing cells) is aspirated from the patient and cultured under various conditions to obtain chromosomes. These are G-banded and analyzed for aneuploidy, translocations, deletions and other abnormalities. Multiple cultures are set up, as the abnormality may not be detected in all cultures. Acquired chromosome abnormalities are occasionally seen in only a few poor quality cells, hence detailed analysis is carried out. However, subtle translocations cannot always be ruled out by karyotyping. Hence FISH is preferable.
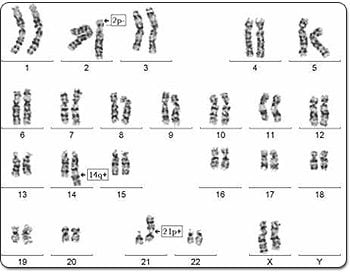
.
A bone marrow karyotype of a patient with CLL (chronic lymphocytic leukemia) showing various chromosome abnormalities.
Sample : The latest WBC count should be sent along with the sample. The quantity of bone marrow required is inversely proportional to the WBC count. For example, 2 ml bone marrow in a sodium heparin vaccutainer is required for a normal WBC count. If the WBC count is low, proportionately more bone marrow may be required. The sample should be transported at room temperature.
The FISH technique is very useful in diagnosis, prognosis, and management of leukemia patients and in the detection of minimal residual disease.
In order to periodically monitor the progress of therapy in BCR/ABL fusion (Philadelphia +ve) and PML/RARA fusion (AML-M3) cases, semi-quantitative FISH can be carried out on heparinized blood instead of bone-marrow. In case a relapse is suspected, karyotyping from bone-marrow can be repeated to look for clonal evolution.
The double-fusion BCR/ABL and PML/RARA probes reduce the chances of false positive results. FISH is also useful in complex translocations leading to a masked Philadelphia chromosome, which may be missed on karyotyping.
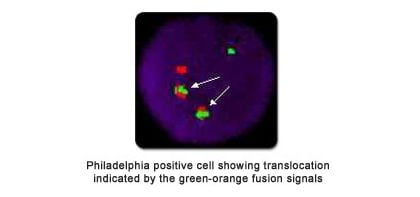
.In Multiple Myeloma, FISH is carried out on immunomagnetically separated CD138 positive plasma cells.
List of FISH Probes in Leukemia used by our lab
- BCR-ABL/Philadelphia or Ph chromosome/t(9;22) for CML, AML, ALL
- PML-RARA / t(15;17) for APML and RARA breakapart rearrangement for APML
- AML1-ETO / RUNX1T1-RUNX1 / t(8;21) for AML
- Inversion 16 (CBFB)/t(16;16) for AML
- t(3;3)/inversion 3/RPN1-MECOM for AML
- MLL (11q23) rearrangement for AML / MDS / ALL / Lymphoma
- Del 5q (EGR1) for MDS / AML
- Del 7q (D7S486) for MDS / AML
- Del 20q (20qter) for MDS / AML
- Trisomy 8 for MDS / AML
- TEL-AML /ETV6-RUNX1 / t(12;21) for ALL
- t(1;19) or TCF3/PBX1 for ALL
- TRAD (14q11.2) rearrangement for T-ALL
- Chr. 12, Del 13q, Del p53 and Del ATM for CLL / Multiple Myeloma
- IGH (14q32) rearrangement for Multiple Myeloma / ALL / Lymphoma
- RB1 (13q) deletion for CLL
- Deletion MYB or deletion 6q for CLL
- t(4;14)/ IGH-FGFR3 for Multiple Myeloma
- t(14;16) / IGH-MAF for Multiple Myeloma
- 1p loss/deletion and 1q gain /amplification for Multiple Myeloma
- PDGFRA and PDGFRB rearrangement for myeloid neoplasm with hyper eosinophilia.
- BCL2 and BCL6 for Lymphoma
- t(14;18)/ IGH-BCL2 for Lymphoma
- Burkitt’s Lymphoma / (8q24) /(c-Myc) rearrangement
Sample: Based on the diagnosis and depending on WBC count 2-3 ml peripheral bone marrow sample (or blood in some cases) in heparin tube (Green top) transported at room temperature. No fasting is needed.
Note: Not all FISH tests will show positive results if set up on a blood sample. Hence, bone marrow is the preferred sample for testing.
In casesof sex-mismatched bone-marrow transplantation, determination of the percentage of XX and XY chimerism by FISH gives an indication of the success of a transplant.
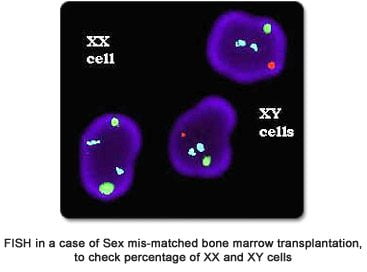
Sample: 2-3 ml Bone marrow / blood in heparin vaccutainer (Green top) with latest WBC count transported at room temperature.
We offer the Vysis UroVysion FISH test to monitor bladder cancer. The test is designed to detect aneuploidy for chromosomes 3, 7, 17, and loss of the 9p21 locus (containing the p16 tumor suppressor gene), which is one of the most common alterations in urothelial carcinoma. Results from the UroVysion Kit are intended for use in conjunction with current standard diagnostic procedures, as an aid for initial diagnosis of bladder carcinoma in patients with hematuria, and subsequent monitoring for tumor recurrence in patients previously diagnosed with bladder cancer.
- UroVysion detects chromosomal abnormalities associated with the development and progression of bladder cancer.
- UroVysion in conjunction with cystoscopy delivers the best balance of sensitivity (97%) and specificity (95%).
- It allows for more accurate patient monitoring, by detecting bladder cancer recurrence up to 6 months sooner than current diagnostic methods.
- It is more sensitive than cytology and reduces false negative results.
- The UroVysion kit detects all stages and grades of bladder cancer. It is highly sensitive for higher grades and stages of tumours.
- The test is not affected by BCG immunotherapy.
Early detection of high grade disease is critical to improve survival.
FISH is carried out in our Centre on formalin fixed paraffin embedded (FFPE) tumor tissues to check for
- Her2/neu amplification in breast, oesophageal and other cancers.
- BCL2, BCL6, IGH and MYC rearrangements in Lymphomas.
This helps in prognostication and choice of therapy.

