Table of Contents
What is a Bulky Uterus?
A bulky uterus is regarded as the general term for an enlarged-shaped uterus. The uterus turns bulky because it grows during the period of pregnancy. In some non-pregnant conditions, the uterus grows due to musculature, its endometrial glands and even through its connective tissue.
It is observed that the normal measurement of a non-pregnant uterus is measured to be around 7 to 8 cm long, 5 cm across and 4 cm thick. Its average volume is estimated to be around 80 and 200 ml. Moreover, there are many reasons for the enlargement of the uterus. One of the most common reasons is that women who bear a child in their womb usually have a large uterus which is measured to be normal. Their uterus intends to become enlarged due to benign conditions and even due to malignancy.
Moreover, the infection of the uterus is also the cause behind its enlargement. Read on to know more about bulky uterus symptoms, causes and treatment.
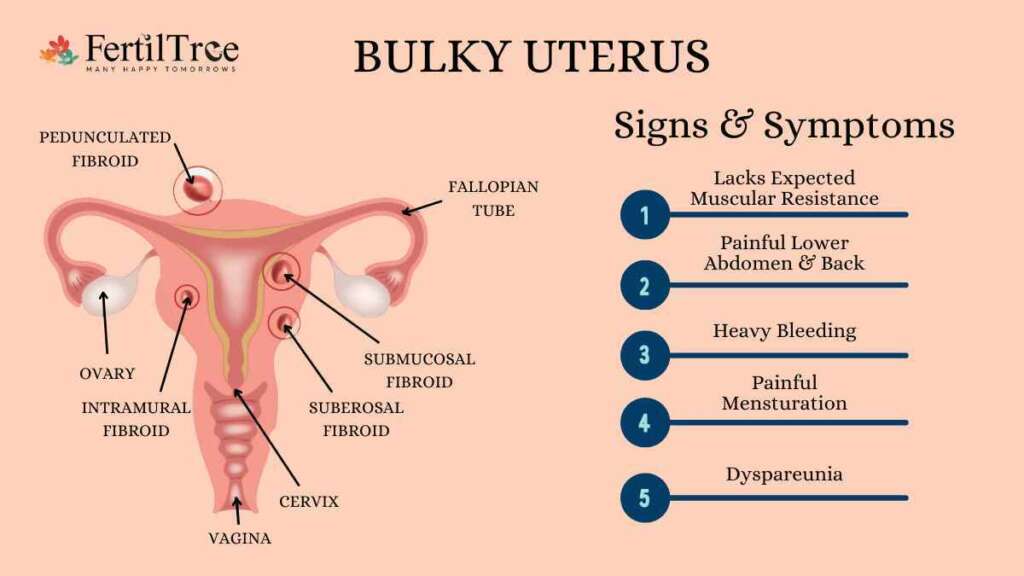
Symptoms of Bulky Uterus
A bulky uterus can be asymptomatic, but it also causes symptoms when it enlarges.
These can result in causing pressure symptoms, a feeling of heaviness, exert pressure over the urinary bladder and cause frequent urination and sometimes even let others face difficulty in urinating. When it happens, women’s periods can become heavier and even longer.
There can also be bleeding occurring between the period cycles. Even during the case of enlargement, the pus in the uterus can also cause foul-smelling discharge, malaise, fever and discomfort.
A bulky uterus is also the cause of infertility, brings failure in early implantation and also causes miscarriage.
There are many causes of the bulky uterus, and the symptoms of it may differ because they are based on the cause behind it.
Some of the common symptoms of bulky uterus include –
- Irregular abnormalities in the menstrual cycle
- Heavy bleeding and cramping in the pelvic region
- Swelling in the uterus
- Backaches
- Bleeding in the postmenopausal period
- Irregular vaginal discharge
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Excess bleeding between periods causing Anemia
- Heaviness around the lower abdomen
- Palpation of a mass around the lower abdomen
- Paleness of the skin
- General weakness
Causes of Bulky Uterus
During the time of pregnancy, the size of the uterus often enlarges to a large extent. Apart from it, several conditions can cause a bulky uterus. There are chances that a woman may suffer from fibroids. PCOS, endometrial cancer, and many more diseases might cause the uterus to expand to a large size.
1. Fibroids
Fibroids are non-cancerous tumors that can grow inside the uterus. These non-cancerous growth tumors are small lumps that measure up to numerous pounds. They may also be responsible for causing pain and heavy menstrual cycles, back pain, bleeding & frequent urination.
Fibroids usually affect those over 30 years of age.
This disease is found commonly among African-American women other than Caucasians. However there is an increasing trend of incidence of fibroids in Indian women. In addition, women suffering who are overweight and obese have a greater risk of developing fibroids. Moreover, uterine fibroids affect millions of women across the world.
There are many causes of fibroids. These could be due to genetic changes, hormones, growth factors and it is believed may be caused by Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals.
Genetic Changes: Many fibroids consist of changes in the genes that remain different from those found in the uterine muscle walls.
Hormones: Estrogen is a hormone that stimulates the development of the uterine lining in each menstrual cycle and during pregnancy. In addition, fibroids contain more estrogen and progesterone receptors than typical uterine muscle cells carry. This estrogen triggers the stimulation and growth of fibroids. This is why fibroids tend to shrink after menopause because of a decrease in hormone production.
The bulkiness caused by the fibroids in the uterus exerts pressure on the bladder and rectum, causing frequent urination and rectal pressure.
Infertility: Fibroids also contribute to infertility in several ways.
Other symptoms of fibroids are –
- Heavy & Frequent Menstrual Bleeding
- Longer duration of Menstrual Period
- Pelvic Pressure or Pain
- Frequent Urination
- Constipation
- Backache and leg pain
Fibroids are known by their location. Intramural fibroids grow within the muscular uterine wall & submucosal fibroids bulge within the uterine cavity.
Moreover, subserosal fibroids project directly to the region outside the uterus.
If a pregnant woman suffers from fibroids, it will not be good for them. This is because it will bring problems in the development of a baby. And even let them face pain during the labor period.
Apart from it, they might witness abdominal pain during pregnancy, and there will also be the risk of premature labor too.
2. Adenomyosis
Adenomyosis is a condition where the uterine lining, that is the endometrium, grows into the uterine musculature. There are several known causes for adenomyosis, the common one being hormonal imbalance and is linked to estrogen levels. It usually occurs in women over the age of 30 years and is often seen in women who are infertile or who have never borne children.
Its incidence increases in the 40’s and is associated with increasingly painful periods, heavy bleeding and abdominal pain. Many women may see the resolution of their symptoms after menopause with the stoppage of estrogen production. Other causes of adenomyosis are genetic mutations and inflammation. Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals can also contribute to Adenomyosis.
Symptoms include –
- Abdominal Bloating & Heaviness
- Heavy Bleeding
- Pelvic Pain
- Severe Cramps During Periods
The diagnosis of Adenomyosis can be mage by several methods:
Pelvic Exam: A Pelvic exam may reveal an increase in the size of the uterus and pain on palpation.
Ultrasound: A transvaginal and abdominal ultrasound aids the diagnosis. The images show a thickening of the uterine wall and loss of the junctional zone that is the junction of the endometrium and the myometrium.
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging): A pelvic and abdominal MRI with or without contrast. The third way to diagnose this test is through (MRI). This scan shows uterine enlargement and the thickening of specific areas. The thickening may be uniform throughout the uterus or be seen as local masses in areas of the uterus.
3. Endometrial Cancer
This disease begins in the layer of cells forming the uterus lining. The malignant cells develop within the endometrial tissue.
Some of the symptoms of endometrial cancer include –
- Bleeding or discharge between periods
- Postmenopausal Bleeding
- Pain During Sexual Intercourse
- Pain or Mass In The Pelvic Area
The diagnosis of Adenomyosis can be mage by several methods:
Endometrial Biopsy
In this diagnostic test, a small and flexible tube is directly inserted into the uterus to gather a sample of endometrial tissue.
This collected sample is further examined under a microscope to observe the growth of cancerous cells occurring within the body.
Transvaginal and Abdominal Ultrasound
These will reveal an increased blood flow to the uterus and irregular enlargement of the uterus. Lymph nodes around the uterus may also be enlarged. A MRI, CT scan and PET CT are other diagnostic tests.
4. Pyometra ( Pus In The Uterus)
Pyometra is the collection of pus in the uterus, extending to the walls and thinning the uterus. This may occur due to an infection in the uterus with narrowing of the cervical canal which prevents the pus from escaping outside the uterine cavity. It can also occur due to a secondary infection of the cancerous tissue in the uterus.
What are the available treatment options for bulky uterus?
The treatment of bulky uterus depends on the cause of the bulky uterus.
What are the treatments available for Fibroids?
Its treatment includes-
1. Anti-inflammatory Medicines: The availability of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, including ibuprofen and mefenamic acid medicines, helps in reducing the body’s production of prostaglandin, which is connected to heavy periods. In addition, anti-inflammatory medicines also act like painkillers.
2. Oral Progestogen Tablets: Oral progestogen tablets reduce the flow of heavy periods.
3. Surgery: Laparoscopic or sometimes open myomectomy and Hysterectomy are the surgical options for removing fibroids. This decision is based on the number and position of the fibroids and the age and fertility status of the woman.
What are the treatment options available for adenomyosis?
Some of the treatments available for adenomyosis include hormonal contraceptives, surgery, and medication. Some women who suffer from mild symptoms can manage adenomyosis in a non-surgical way. Progesterone tablets or injections, GnRH analogues and GnRH antagonists are used in the treatment of adenomyosis. Women suffering from severe intractable symptoms may need a hysterectomy.
Diagnosis of a Bulky Uterus?
Palpation, Pelvic and Abdominal 2D, 3D and 4 D Ultrasound is helpful. In some cases a MRI, CT or a PET CT may be recommended.
What are the complications of a bulky uterus?
- Pain & Pressure Over The Pelvic Region: The enlarged uterus can exert pressure over the organs lying within its vicinity. It can cause frequent urination, swelling, bloating and cramps in the pelvic area.
- Infertility: Fibroids and adenomyosis can cause an increased chance of infertility and miscarriage.
- It has been found in a study that nearly 10% of women suffering from fibroids can suffer from infertility.
- Excessive Bleeding: Adenomyosis and fibroids can result in heavy menstrual and intermenstrual bleeding.
Impact Of Bulky Uterus on Fertility
A bulky uterus caused due to adenomyosis or multiple fibroids can contribute to infertility and alters endometrial function. It also reduces the implantation and pregnancy rate among women undergoing IVF. Thus, it will be advisable for you to connect with infertility specialists to treat the cause of this disease.
Read more: Why does IVF fail? Top Reasons For IVF Failure
When To See Your Doctor
If you have symptoms due to a bulky uterus as listed above, or you are having difficulty in conceiving, it is best to see your fertility doctor.
FAQs on Bulky Uterus Causes, Treatment and Diagnosis
Can I get pregnant with a bulky uterus?
If the uterus is physiologically enlarged may due to past pregnancies it is not difficult to get pregnant. If the uterus is enlarged due to small fibroids, it may not be difficult to get pregnant. Mild Adenomyosis does not generally prevent a pregnancy from occurring. However, if a mildly enlarged uterus is associated with other conditions like endometriosis, it may prevent a natural conception.
Should an enlarged uterus be removed?
A mildly enlarged uterus does not require removal. Removal of the uterus, called hysterectomy, may be necessary in cases of significant fibroids and large adenomyotic uterus causing symptoms in a woman who has already borne children.
For those women trying to conceive, a conservative approach like the removal of the adenomyoma or the fibroids is preferred. A hysterectomy should be performed if a woman has completed childbearing and is symptomatic. Removing the ovaries in younger women is unnecessary as this can cause early surgical menopause, which can affect the woman’s health. Endometrial cancer warrants a total radical hysterectomy.
Can an enlarged uterus cause constipation?
By and large, an enlarged uterus does not cause constipation. Very rarely, an enlarged uterus which is retroverted or has associated endometriosis can cause irritation of the bowels and difficulty and painful defecation.
I have large Uterine Fibroids. Is It possible to have a non-operative procedure? Kindly let me know.
If you are not planning to have children, then there is a procedure called Focused ultrasound energy that is used to shrink the fibroids, MRgFUS (Magnetic Resonance Imaging Focussed Ultrasound). However, it is not recommended for multiple large fibroids and may not be useful for women trying to conceive.
Another method is uterine artery embolisation which decreases the blood supply to the fibroids, thereby shrinking them. Again this procedure should not be performed on women trying to conceive. GnRH analogues (Gonadotropin hormone-releasing analogues) and, more recently, oral GnRH antagonists can help women who are not candidates for surgery or do not wish to undergo surgery.
Is Adenomyosis a tumor?
Adenomyosis is a general enlargement of the uterus caused by the growth of endometrial glands within the musculature of the uterus. Sometimes the Adenomyosis may be localized to some parts of the uterus, forming what is called Adenomyosis. These look like fibroids but are distinctly different.
As per my scan reports, my uterus is bulky. What treatment plan should I follow?
The treatment will depend on your age, your desire to have children and the reason for the bulkiness of the uterus. Also, if the bulkiness is symptomatic or not and whether it is likely to cause problems in the future.
Can a bulky uterus cause pregnancy complications?
Yes, a very bulky uterus can cause the failure of proper implantation, bleeding, separation of the placenta, cramping of the uterus, torsion of the uterus, premature delivery and complications during delivery.
Is a bulky uterus dangerous?
A slight enlargement is not dangerous. However, significant enlargement can cause the complications listed above.